Textiles play a range of roles in all of our lives and therefore come in many forms. Traditionally, the textile discipline has been split into distinct areas of constructed and printed textiles, although these categories include many means of making.
Constructed textiles can be made through knitting (by machine or hand),through weaving or through other processes where fibres or chemicals are united, extruded or bonded to create a pliable material. Knitting and weaving is still the most efficient and successful means of creating sufficient quantities of textiles for our needs, but modern technology (3D printing) has also meet our personal demands more.

https://study.com/academy/lesson/constructed-textiles-techniques.html
Printing textiles and employing other embellishment and textiles finishing techniques, i.e. embroidery, laminating, or coating allows us to apply further aesthetic qualities onto the surface of a textile or to alter the qualities a constructed textile possesses.

https://blog.drupa.com/de/digital-wool-printing/
Material life cycle: The concept of material life cycle has become extremely relevant in. a world thats increasingly ware of wastefulness, longevity and our individual consumption of products. Creating textiles or any product forces the designer, manufacturer, and maker to consider what the consequences of that product will ultimately be.
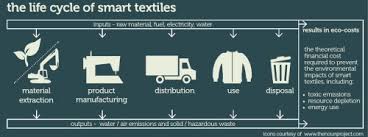
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0264127515300174
Stages of textile product life cycle:
- Agriculture/ raw fibre production
- Ginning
- Spinning
- Weaving
- Processing
- Stitching
- Distribution/ retail
- Use/ consumption and end of life
Spinning is the action of converting cotton fibres into yarn. (my own definition).
Spinning: the action or process of spinning; the conversion of fibres into yarn. https://www.lexico.com/en/definition/spinning
The Spinning Jenny was a machine invented in the early Industrial Revolution that was one of the key developments in industrialization. It is a multi-spindle spinning frame invented by James Hargreaves in 1764. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Spinning_jenny
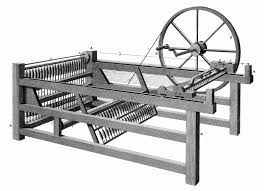
https://www.britannica.com/technology/spinning-jenny
Weaving (I couldn’t think of my own definition).
Weaving: the craft or action of forming fabric by interlacing threads. https://www.lexico.com/en/definition/weaving
Three types of weaving: plain, twill and satin. (there are more types but these are just some examples.
Plain weave each filling yarn passes over and under the warp yarns, with the order reversed in alternating rows.
Twill weaves are made by interlacing the yarns in a manner producing diagonal ribs, ridges, or wales across the fabric.
Satin weaves have a sheen produced by exposing more warps than fillings on the right side of the fabric.
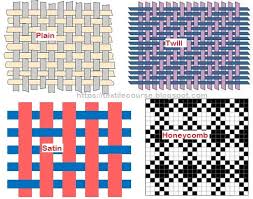
https://textilecourse.blogspot.com/2018/08/basic-weaves-structures.html